Archives
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-04
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
This finding is consistent with our observations in
2018-11-06
This finding is consistent with our observations in human fetal RG cells (Mo and Zecevic, 2008), indicating that in both cell populations Pax6 affects proliferation as well as neuronal fate. Numerous studies have reported the successful transplantation of hESC into rodent brains (Kelly et al., 200
-
Generally histone modifications facilitate protein protein i
2018-11-06
Generally, histone modifications facilitate protein–protein interactions with effector proteins or readers. Bromodomains interact with acetyl-lysines, while chromodomains, plant homeodomains (PHD), and others associate with methyl-lysines. Interestingly, H2AZ-containing nucleosomes associate with se
-
We identified CaMKII as a downstream target of
2018-11-06
We identified CaMKII as a downstream target of NMDA receptors activated in NPCs following TLQP-62 treatment. CaMKII can associate with NMDA receptors and ultimately sustain its activation state (Bayer et al., 2001). Supporting our novel findings for a role of CaMKII in neurogenesis is a study showin
-
As METH impairs self renewal capacity
2018-11-06
As METH impairs self-renewal capacity, we also explored the influence of METH in DG stem cell-fate division, a suitable method to characterize the phenotype of cells that are derived from the division of one DG stem cell. Indeed, a stem cell can undergo symmetric cell division towards self-renewal,
-
Taken together we conclude that Lats may regulate adult
2018-11-06
Taken together, we conclude that Lats may regulate adult cardiomyocyte hypertrophy independent of Yap or Tead1. Rather than controlling cardiac hypertrophic growth, the canonical Hippo/Yap pathway is crucial for regulation of cardiomyocyte survival in the adult heart. This parallels the findings in
-
br Materials and methods br Author disclosure
2018-11-06
Materials and methods Author disclosure statement Acknowledgments This work was supported by grants from the “Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red en enfermedades raras” (CIBERER) (Grant 13-717/132.05 to RG), the “Instituto de Salud Carlos III” (FIS PI10/0703 and PI13/00556 to RG and PI
-
br Acknowledgements br Resource table br Resource details
2018-11-06
Acknowledgements Resource table Resource details To generate the Saudi KACST induced Pluripotent Stem Cell line No 1 (SKiPSc1) cell line, four reprogramming Yamanaka factors (Oct3/4, Sox2, c-Myc, and Klf4) (Takahashi et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2007) were delivered to HNFFs by Sendai viral inf
-
br Funding This work was partially supported by
2018-11-06
Funding This work was partially supported by grants from: ERC-2013 AdG MUNCODD GA340172, AriSLA full grant 2014ARCI, Epigen Flagship Project EPIGENOMICS, AFM TelethonGA17835, Fondazione Roma and Parent Project to I.B. Conflict of interest Author contributions Acknowledgments Introduct
-
The bromodomain and extraterminal BET family of bromodomain
2018-11-06
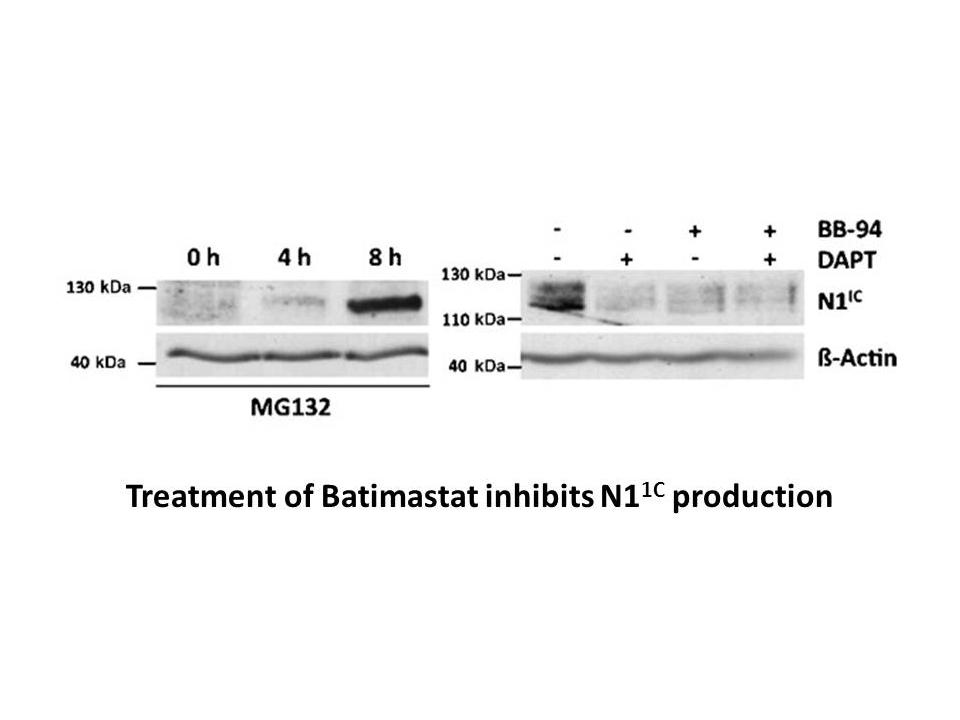
The bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) family of bromodomain-containing proteins (Brds), including Brd2, Brd3, Brd4, and testis-specific BrdT, are epigenetic readers of the acetylation histone code on chromatin. The two tandem bromodomains of BET proteins bind acetylated lysine in histone N-termina
-
These results with fresh non fractionated not culture expand
2018-11-06
These results with fresh, non-fractionated, not culture-expanded, adipose tissue-derived SVF are comparable with other two previously reported clinical series, using cultured adipose-derived ADSCs with controlled cell doses. The adipose tissue contains large populations of mesenchymal AM966 (ADSCs)
-
br Introduction Human leukocyte antigen G
2018-11-06
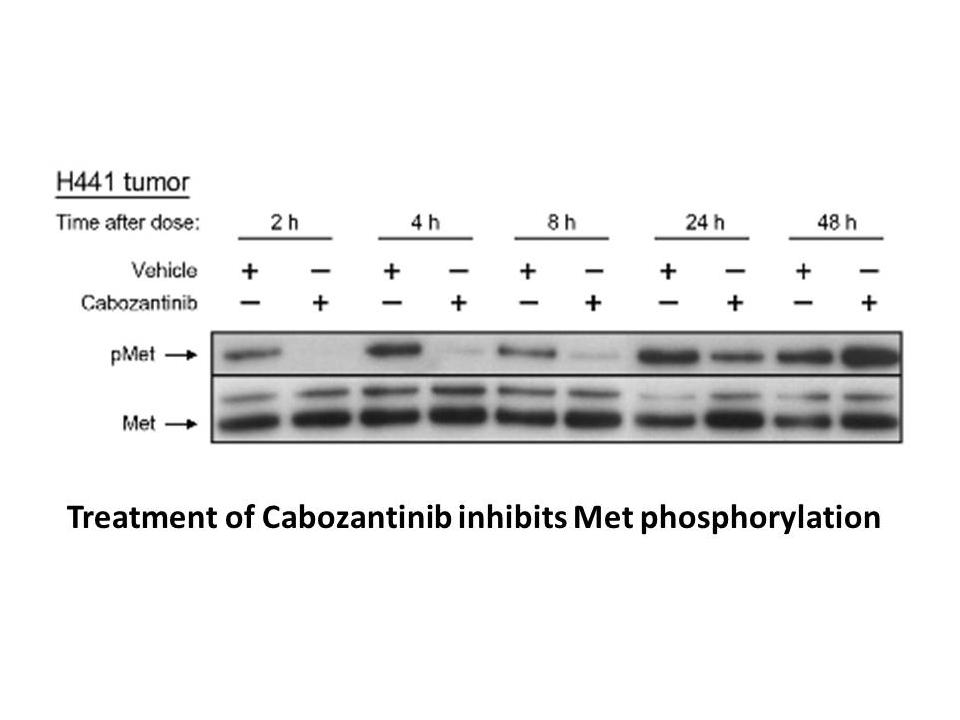
Introduction Human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G) belongs to the non-classical HLA class I bms-690514 and is a tolerogenic molecule that acts on cells of both innate and adaptive immunity. Besides its immunosuppressive function in transplantation, autoimmunity and tumour progression, HLA-G expressi
-
The concept of neoblast specialization at
2018-11-06
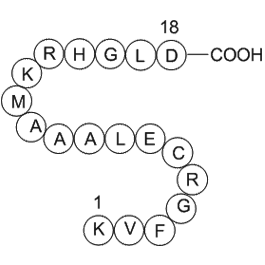
The concept of neoblast specialization at wounds is important in understanding planarian regeneration and opens many avenues for future inquiry. For example, how is the neoblast response tailored to the identity of missing tissues? Do specialized neoblasts amplify their population, or do specialized
-
In conclusion the Olfm IRES eGFPCreERT allele
2018-11-06
In conclusion, the Olfm4-IRES-eGFPCreERT2 allele described here provides a tool, separate from Lgr5, that can be used to further characterize intestinal stem cells. Experimental Procedures Acknowledgments We thank Hugo Snippert for analysis of the Olfm4 animals and Valentina Sasselli for a cr
-
Only pro inflammatory macrophages M M
2018-11-05
Only pro-inflammatory macrophages (M1MФ) formed a functional synapse with MSCs, which suggests that the MSC response depends on the macrophage phenotype. The link between the macrophage phenotype and functional synapse was demonstrated in previous work. For instance, F-actin clusters were detected a
-
Macrophages key elements of initiation and control of
2018-11-05
Macrophages, key elements of initiation and control of inflammation (Mantovani et al., 2013), can be polarized in response to their microenvironment and adapt their function during the different phases of the immune response. Macrophages are typically divided into two types: classically activated ma
15971 records 1048/1065 page Previous Next First page 上5页 10461047104810491050 下5页 Last page